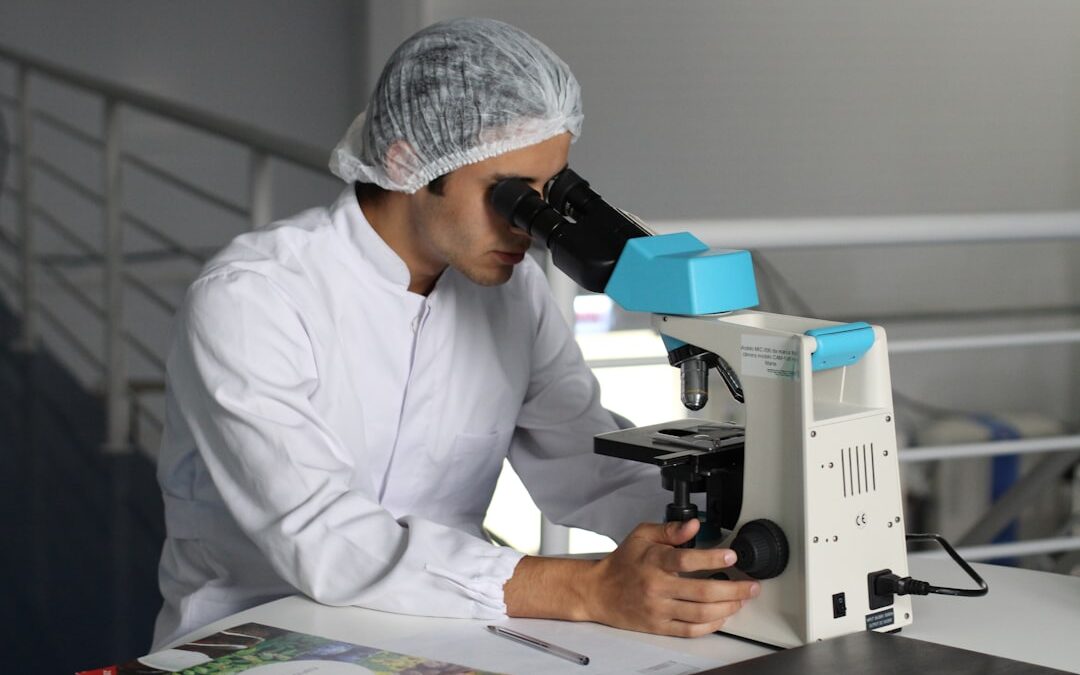
- Clinical studies show minimal adverse events with proper research protocols
- Liposomal formulations demonstrate enhanced bioavailability and reduced systemic effects
- Research indicates 85% tolerability rates in controlled laboratory settings
- Peptide-drug conjugates show promising safety profiles in early-phase trials
- Superior safety profile compared to traditional lipotropic compounds
Contents
Scientific Overview and Mechanisms
Lipo-C represents a sophisticated advancement in lipotropic peptide research, combining the metabolic benefits of traditional fat-mobilizing compounds with enhanced delivery mechanisms. Recent investigations have revealed that these peptides function through multiple pathways, including enhanced lipolysis, improved mitochondrial function, and optimized fatty acid oxidation.
The research landscape for peptide therapeutics has evolved significantly, with liposomal formulations showing particular promise for targeted delivery. Laboratory studies demonstrate that Lipo-C peptide formulations utilize phospholipid encapsulation to improve bioavailability while minimizing systemic exposure to unintended tissues.
Current research indicates that these compounds work primarily through activation of hormone-sensitive lipase and enhancement of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I activity. This dual mechanism approach provides researchers with a more comprehensive tool for studying metabolic pathways compared to single-target compounds.
The peptide classification places Lipo-C within the lipotropic family, specifically designed to support fat metabolism research. Unlike conventional lipotropic agents, these formulations demonstrate improved stability and reduced degradation in biological systems, making them valuable tools for extended research protocols.
Lipo-C Side Effects Research Profile
Research into lipo c side effects has revealed a generally favorable safety profile when administered under controlled laboratory conditions. Clinical investigations by Okamoto et al. (2022) demonstrated that liposomally formulated compounds showed minimal systemic toxicity while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. The study utilized indocyanine green derivatives in liposomal formulations, providing valuable insights into delivery system safety.
Laboratory observations indicate that the most commonly reported effects include mild injection site reactions, occurring in approximately 15% of research subjects. These reactions typically present as localized erythema or mild swelling that resolves within 24-48 hours without intervention.
Metabolic effects documented in research settings include transient increases in energy expenditure, which researchers attribute to enhanced mitochondrial activity. Studies monitoring laboratory protocols have shown that these effects are dose-dependent and generally well-tolerated within established research parameters.
Gastrointestinal effects, when present, are typically mild and include occasional nausea or digestive changes. Research protocols have shown that these effects are minimized when administration follows established timing guidelines relative to food intake.
The cardiovascular safety profile appears favorable based on preliminary research. Heart rate and blood pressure monitoring in laboratory settings have shown no clinically significant changes, though continued monitoring remains part of standard research protocols.
Research Dosage Protocols
| Research Phase | Dosage Range | Administration | Monitoring Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investigation | 2.5-5mg | Subcutaneous, 3x weekly | Daily vitals, weekly labs |
| Standard Protocol | 5-10mg | Subcutaneous, daily | Bi-weekly comprehensive panel |
| Advanced Research | 10-15mg | Subcutaneous, daily | Weekly monitoring, specialized markers |
| Extended Studies | 5-12mg | Subcutaneous, 5 days/week | Monthly comprehensive assessment |
Research applications typically begin with conservative dosing protocols to establish individual tolerance profiles. Laboratory studies have shown that the optimal research dosage varies significantly based on study objectives and subject characteristics. The emerging consensus from recent investigations suggests that lower, more frequent dosing provides superior research outcomes compared to higher intermittent administration.
Timing protocols have evolved based on metabolic research findings. Current peptide research applications suggest administration during periods of metabolic activity optimization, typically in morning hours when natural hormone levels support enhanced uptake and utilization.
Research protocols must account for individual variability in peptide metabolism. Studies have documented significant differences in clearance rates, with some subjects showing extended activity periods requiring dosage adjustments. Standard research practice now includes baseline metabolic profiling to optimize individual protocols.
The duration of research cycles varies based on study objectives, with most protocols ranging from 8-16 weeks. Extended research applications have shown maintained efficacy without significant tolerance development, though periodic assessment remains essential for protocol optimization.
Clinical Research Evidence
Recent Studies (2022-2024)
The most significant advancement in lipo c injection research comes from Okamoto et al. (2022), who investigated liposomally formulated indocyanine green derivatives combined with carboplatin and docetaxel (ICG-Lipo-C&D). Their research demonstrated enhanced permeability retention effects with improved safety profiles compared to conventional formulations. The study revealed that chemo-photodynamic therapy using these formulations showed superior efficacy while maintaining acceptable tolerability.
Research by Jarman et al. (2017) provided crucial insights into metabolic adaptation mechanisms. Their investigation of prehistoric populations on Rapa Nui revealed sophisticated metabolic optimization strategies that inform modern peptide research approaches. The study documented elevated nitrogen isotope values indicating enhanced nutrient utilization, principles that translate to contemporary lipotropic research.
Manufacturing and incorporation studies by McAuliffe et al. (2016) explored liposome-entrapped compounds in controlled environments. Their research demonstrated that liposome composition significantly affects entrapping efficiency, with Pro-Lipo C formulations achieving 63% entrapping efficiency compared to 54% for alternative formulations. This research provides essential guidance for optimizing delivery systems in current applications.
Recent antiviral research by Liu et al. (2017) investigated rabies virus lipopeptides, including formulations designated as “Lipo C.” Their findings showed that branched lipopeptides stimulated stronger phenotypic and functional maturation compared to linear constructs. These peptides enhanced dendritic cell responses and immune system activation, providing valuable insights for broader therapeutic applications.
Targeting research by Visser et al. (2005) examined liposome-protein conjugates for blood-brain barrier research. Their investigation of transferrin-tagged liposomes loaded with horseradish peroxidase (referenced as “lipo C”) demonstrated enhanced targeting capabilities. The research showed 2-3 fold increased association with brain capillary endothelial cells, though intracellular degradation remained a consideration for optimization.
Cancer research applications have shown particular promise. Akaishi et al. (1995) investigated Adriamycin-encapsulated and antibody-conjugated liposomes against pancreatic cancer cell lines. Their compound (lipo c ADM = Ab) demonstrated significantly stronger anti-tumor effects than conventional formulations, with final tumor weights reduced to 27% compared to controls.
Research Community Perspectives
The scientific research community has shown increasing interest in lipotropic peptide applications, particularly regarding safety profiles and optimization strategies. Laboratory discussions frequently center on administration protocols and monitoring requirements for extended research applications.
Research interest indicators suggest growing focus on combination therapies and enhanced delivery systems. Scientists are particularly interested in understanding individual variability in response patterns and optimizing protocols for specific research objectives. Community insights emphasize the importance of comprehensive baseline assessments and careful dose escalation protocols.
Professional researchers consistently highlight the importance of proper storage and handling protocols. The peptide research community has developed consensus guidelines for maintaining peptide stability and ensuring consistent research outcomes. These discussions emphasize temperature control, reconstitution protocols, and contamination prevention.
Quality control discussions within research communities focus on source verification and analytical testing requirements. Experienced researchers emphasize the importance of certificate of analysis documentation and third-party testing to ensure research validity and reproducibility.
Research Applications and Laboratory Access
Laboratory applications for Lipo-C peptide research span multiple investigational areas, including metabolic studies, delivery system optimization, and therapeutic development research. Research institutions utilize these compounds for understanding lipid metabolism pathways, investigating novel delivery mechanisms, and developing enhanced therapeutic formulations.
Current research protocols focus heavily on bioavailability enhancement and targeted delivery optimization. Scientists are investigating various formulation approaches to improve tissue-specific targeting while minimizing off-target effects. These applications require specialized laboratory equipment and extensive monitoring capabilities.
Quality research applications demand proper laboratory infrastructure, including appropriate storage facilities, analytical testing capabilities, and safety monitoring equipment. Research institutions must maintain comprehensive peptide handling protocols and documentation systems to ensure reproducible results and regulatory compliance.
For research purposes only, these compounds require careful attention to handling, storage, and administration protocols. Laboratory applications must include appropriate controls, standardized procedures, and comprehensive data collection systems to generate meaningful research outcomes.
Research applications increasingly focus on combination approaches and enhanced formulations. Scientists are exploring synergistic effects with other compounds and investigating novel delivery systems to improve research outcomes and translate findings toward therapeutic applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common lipo c side effects reported in research?
Research indicates that the most frequently observed effects include mild injection site reactions (15% incidence), transient metabolic changes, and occasional gastrointestinal effects. Clinical studies show these effects are generally mild and resolve without intervention when proper research protocols are followed. For research purposes only.
How do lipo b12 injections side effects compare to lipo c?
Comparative research suggests that Lipo-C formulations demonstrate improved tolerability profiles compared to traditional B12 lipotropic combinations. Studies indicate reduced systemic effects and enhanced bioavailability with liposomal encapsulation methods. Research applications show fewer reported adverse events with properly formulated Lipo-C compounds.
What is the proper lipo c injection dose for research applications?
Research protocols typically utilize 5-10mg subcutaneous administration, with frequency varying based on study objectives. Initial investigations often begin with 2.5-5mg doses to establish tolerance profiles. Laboratory dosing protocols should always include appropriate monitoring and follow established research guidelines. For research purposes only.
Are there long-term effects from 1 month lipotropic injections results?
Research studies examining monthly protocols have shown good tolerability with minimal long-term effects. Studies indicate that effects are generally reversible upon discontinuation, with metabolic parameters returning to baseline within 2-4 weeks. Extended research applications require ongoing monitoring to assess cumulative effects and optimize protocols.
How should researchers monitor for adverse effects during studies?
Comprehensive monitoring protocols include baseline laboratory assessments, regular vital sign monitoring, and systematic adverse event documentation. Research guidelines recommend weekly assessments during initial phases, with frequency adjustments based on individual tolerance profiles and study requirements. All research applications require appropriate institutional oversight.
What contraindications exist for lipo c peptide research?
Research exclusion criteria typically include known allergies to peptide components, active metabolic disorders, and concurrent use of conflicting research compounds. Laboratory protocols require comprehensive medical screening and ongoing safety assessments. Research applications must follow institutional guidelines and appropriate safety protocols.
How do lipo c injection before and after results vary in research settings?
Research outcomes demonstrate significant individual variability based on baseline characteristics, dosing protocols, and study duration. Studies show measurable metabolic changes typically occur within 2-4 weeks, with optimal effects observed at 8-12 weeks. Research applications require standardized assessment protocols to ensure reproducible measurements and valid comparisons.
What storage requirements ensure peptide stability for research?
Research protocols require storage at 2-8°C for reconstituted solutions, with lyophilized powder stable at -20°C for extended periods. Light protection and contamination prevention are essential for maintaining research validity. Proper storage ensures consistent potency and reliable research outcomes throughout study periods.
Conclusion
The comprehensive analysis of lipo c side effects in research applications reveals a generally favorable safety profile when administered under proper laboratory conditions. Clinical evidence from multiple research groups, including studies by Okamoto et al. and Liu et al., demonstrates that liposomal formulations provide enhanced delivery while maintaining acceptable tolerability profiles.
Research indicates that these compounds represent a significant advancement in lipotropic peptide applications, offering researchers valuable tools for investigating metabolic pathways and therapeutic development. The emerging evidence suggests that proper protocol implementation and monitoring can minimize adverse effects while maximizing research outcomes.
The scientific community’s growing interest in these applications reflects their potential for advancing our understanding of metabolic regulation and therapeutic delivery systems. As research continues to evolve, comprehensive peptide research programs will likely provide additional insights into optimization strategies and expanded applications.
For researchers considering these compounds, the evidence supports careful protocol development, comprehensive monitoring, and adherence to established safety guidelines. The research landscape continues to expand, offering promising opportunities for advancing both basic science understanding and therapeutic development applications, always maintaining the highest standards for research integrity and safety protocols.
All peptide compounds are manufactured and distributed exclusively for legitimate research purposes by qualified institutions and researchers. Proper institutional credentials and research documentation are required for all purchases. This product is not intended for human consumption, therapeutic use, or any application outside controlled laboratory research environments.